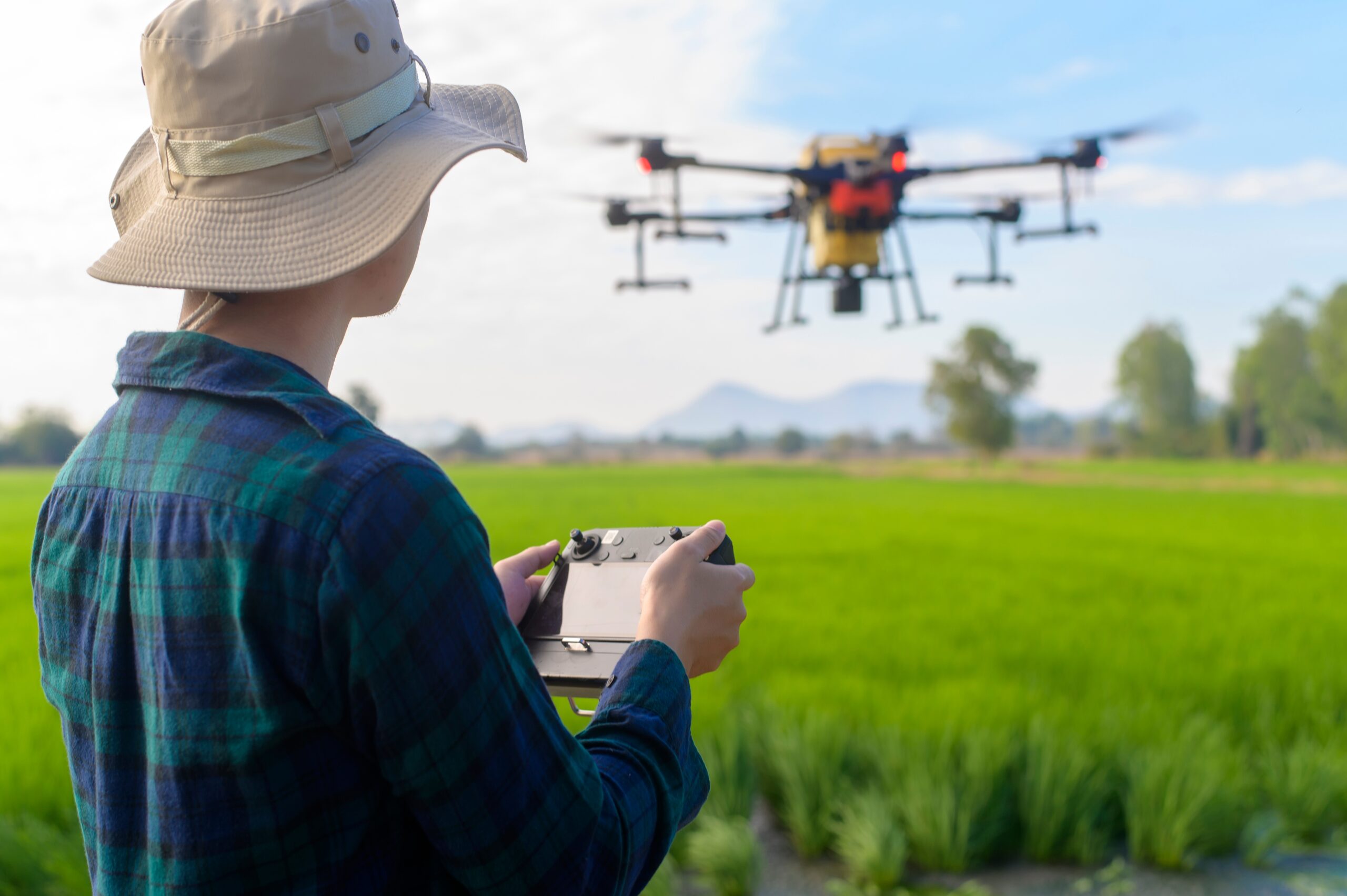
Why do we need IoT in Smart Farming?
A forecast by the food and agriculture arm of the United Nations (FAO) says that the food production worldwide should see a 70% increase by 2050 to cater the ever growing population. And the experts believe that IoT could play a crucial role in meeting this need. Combined with big data, it can do so by improving the efficient use of inputs like soil, fertilizers and pesticides, monitoring the livestock, predicting diseases, scanning storage capacities like water tanks, and making sure that crops are fed and watered well. It shows an overall potency to increase the productivity with a reduced cost.
How is Big Data and IoT being used in agriculture:
While we talk about various interesting aspects that IoT can bring about in agriculture, it gets our curiosity high about how that can be achieved? Well, the most important aspect of it is big data. The data collected from a variety of sensors ensure that all the operations are executed well. Let’s take the use of IoT to monitor health of livestock into account. The farmers can track animals’ movement to establish grazing patterns and hence help increase yield.
In the same way, IoT has the potential to address issues such as irrigation and productivity wherein the data gathered by IoT sensors have the ability to provide an overall performance of the crops and hence determining when the crops might require servicing.
At other instances, real-time data about soil, air quality, water levels etc. can help farmers in making a much informed decision about planting and harvesting crops, thereby increasing the overall yield of the crops.
Challenges faced in IoT applications:
Though it is has been a trend in developed nations, despite being an agricultural nation, countries such as India faces various challenges while applying IoT in agriculture. To begin with, internet connectivity and availability is one of the major challenges. Then there are certain other aspects such as presumption among-st the vendors about Indian consumers not being “ready” for the advanced products. This results in drastically low awareness of IoT devices and systems amongst consumers. That’s not all, the infrastructure required for smooth functioning of the IoT devices, such as smart grids and traffic systems are far from ready, hindering the growth furthermore.
Conclusion:
Despite being a newer concept in the field, there has been a tremendous popularity in the agricultural circuits about the benefits of smart farming and the applicability of IoT. It has been looked upon as a hope to encourage innovation in agriculture with “connected farms” speculated to be the future of farming.
If we talk about the India perspective, with its experience in IP design and project management, it shows up unique potential to come up with innovative products. And with the government initiatives like “Make in India” and “Smart India”, Internet of Things could be utilized to make the best out of our agricultural potential make it smart farming.