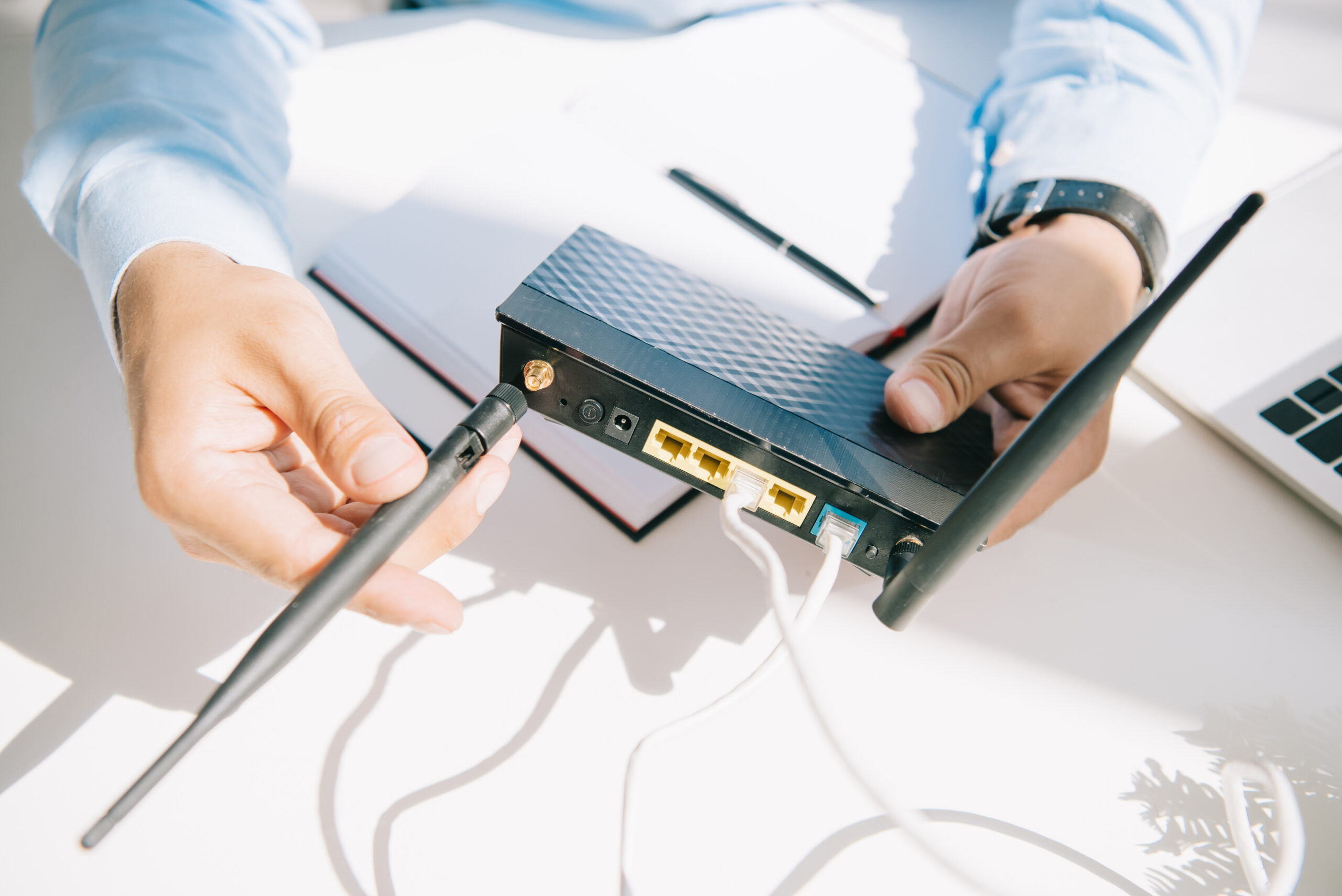
What is OpenWrt?
OpenWrt is a Linux distribution for your router. Like other Linux distributions, it offers a built-in package manager that allows you to install packages from a software repository. It can be used for anything that an embedded Linux system can be used for, including functioning as an SSH server, VPN, traffic-shaping system, or even a BitTorrent client. @benison Tech
OpenWrt isn’t the ideal solution for everyone’s needs. Most people will be happy with their router’s default firmware, while many power users will want a drop-in replacement firmware like DD-WRT. OpenWrt is more flexible – it’s basically an embedded Linux distribution that can be installed on various routers. OpenWrt has a web interface, but if you just want a web interface with more features, you’re probably better off with another replacement router firmware. @benisontech
Like DD-WRT, OpenWrt is Linux-based and may be more stable than the firmware some routers include, which can struggle when handling large numbers of connections.
Uses for OpenWrt
If the idea of having a modular Linux distribution available on your router doesn’t excite you with all the possibilities, you may be reading the wrong article. But we’ll give you a list of the cool things you could do with OpenWrt , aside from having it function as a router:
- Use the SSH Server for SSH Tunneling: OpenWrt includes an SSH server so you can access its terminal. If you expose the SSH server to the Internet (be sure to secure it with key-based authentication instead of a weak password), you can access it remotely and use SSH tunneling to forward your traffic over the encrypted connection. This allows you to securely access websites from public Wi-Fi and access websites that can only be accessed in your home country while travelling abroad.
- Set Up a VPN: SSH tunneling works similarly to a VPN in many ways, but you could also set up a proper VPN on your OpenWrt router.
- Install a BitTorrent Client: With some sort of network-attached storage or a router with an integrated USB port and an attached USB storage device, you could use your router itself as a BitTorrent client.
- Run Server Software: OpenWrt’s software repositories contain packages allowing it to function as a web server, IRC server, BitTorrent tracker, and more. You’re probably already using a router, so why not have that same router function as a server? Routers use much less power than computers, so this is a smart move if you need a lightweight server.
- Perform Traffic-Shaping and QoS: OpenWrt allows you to perform traffic-shaping and quality of service on the packets travelling through your router, prioritizing certain types of traffic. You could even prioritize traffic going to specific computers, de-prioritizing traffic going to other computers.
- Create a Guest Network: OpenWrt’s wiki contains instructions for setting up a special wireless network for guests, one that’s separate from your main network for security purposes. You can even throttle the guest network’s speed.
- Capture and Analyze Network Traffic: You can use tcpdump to log all the packets travelling through your router to a network share and open the file with a tool like Wireshark to analyze your network’s traffic.
This isn’t a complete list, not by a long shot – but it should get you started thinking about what’s possible with OpenWrt. It’s an embedded Linux system with a wide variety of software packages available for it, and in many ways it’s as flexible as a computer running Linux – although its hardware is much more constrained.
Installing OpenWrt
OpenWrt was originally developed for the Linksys WRT54G, but it now supports many more models of routers. You can find a list of supported router models on OpenWrt’s website. OpenWrt’s wiki also offers instructions for installing OpenWrt. While installing OpenWrt, you’re essentially replacing your router’s built-in firmware with the OpenWrt Linux system. for more information regarding Openwrt visit www.benisontech.com